Pigmentary disorders typically result from increased amounts of melanin leading to darker pigmentation, known as hyperpigmentation, or decreased or absent melanin causing a lighter or white appearance, known as hypopigmentation. Pigmentary disorders can be either genetic or acquired.
A common pigmentary disorder seen in the clinic is vitiligo. Vitiligo is an acquired skin disorder which results from the loss of melanocytes, which results in complete loss of pigment. Vitiligo affects approximately 1% of the population and both genders equally. Vitiligo can appear at any age but usually appears before the age of 30. Some patients have a family history of vitiligo and it is occasionally associated with autoimmune disorders.
In vitiligo, there is complete loss of pigment in areas of the skin, and manifests as white patches on skin. Common hypopigmentation conditions that present with light colored patches or spots include pityriasis alba, tinea versicolor, and post-inflammatory hypopigmentation.
Darker spots or patches on the skin are usually a result of hyperpigmentation. Examples of common types of skin hyperpigmentation include melasma, solar lentigines, freckles, post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation and café-au-lait macules etc.
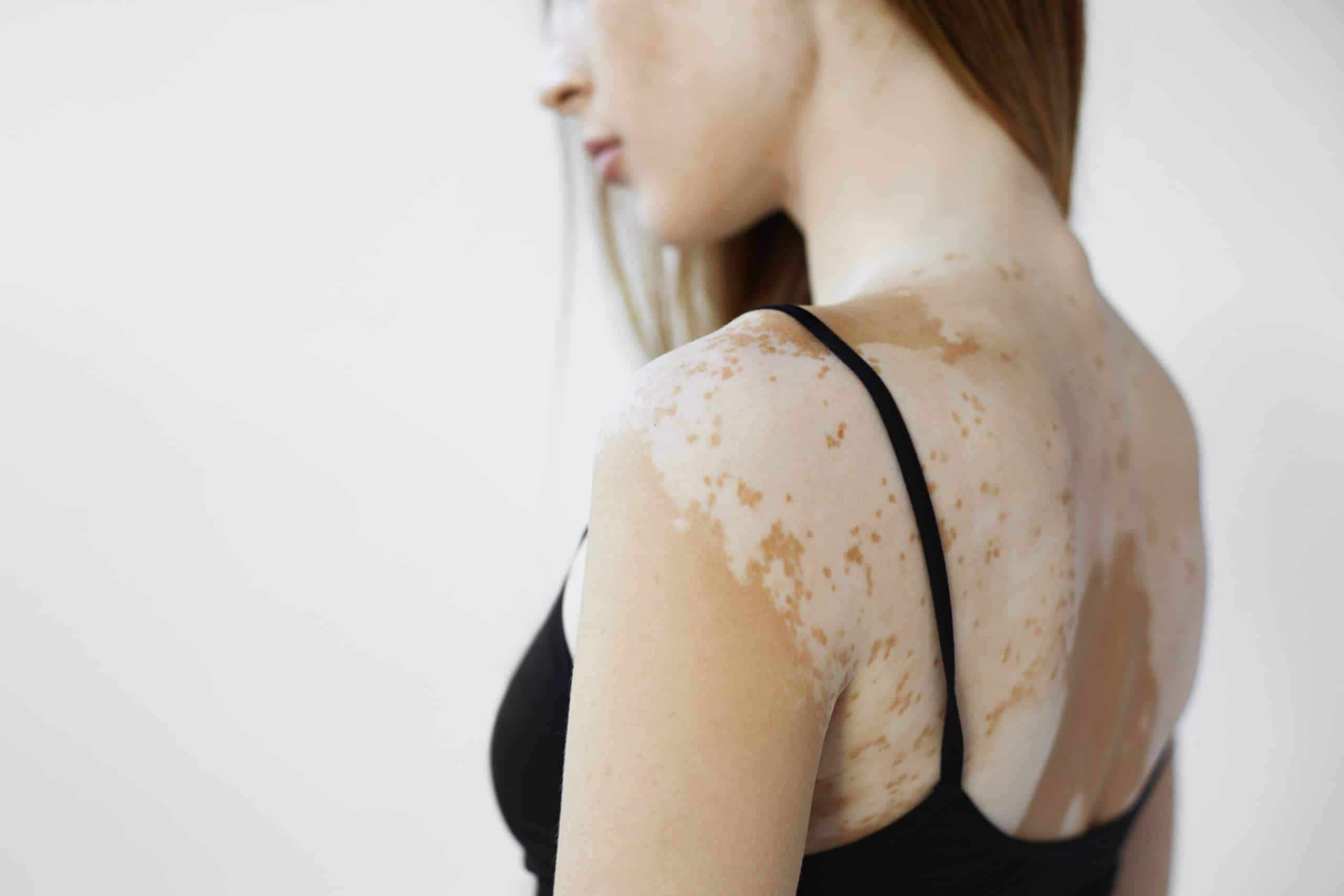

Vitiligo
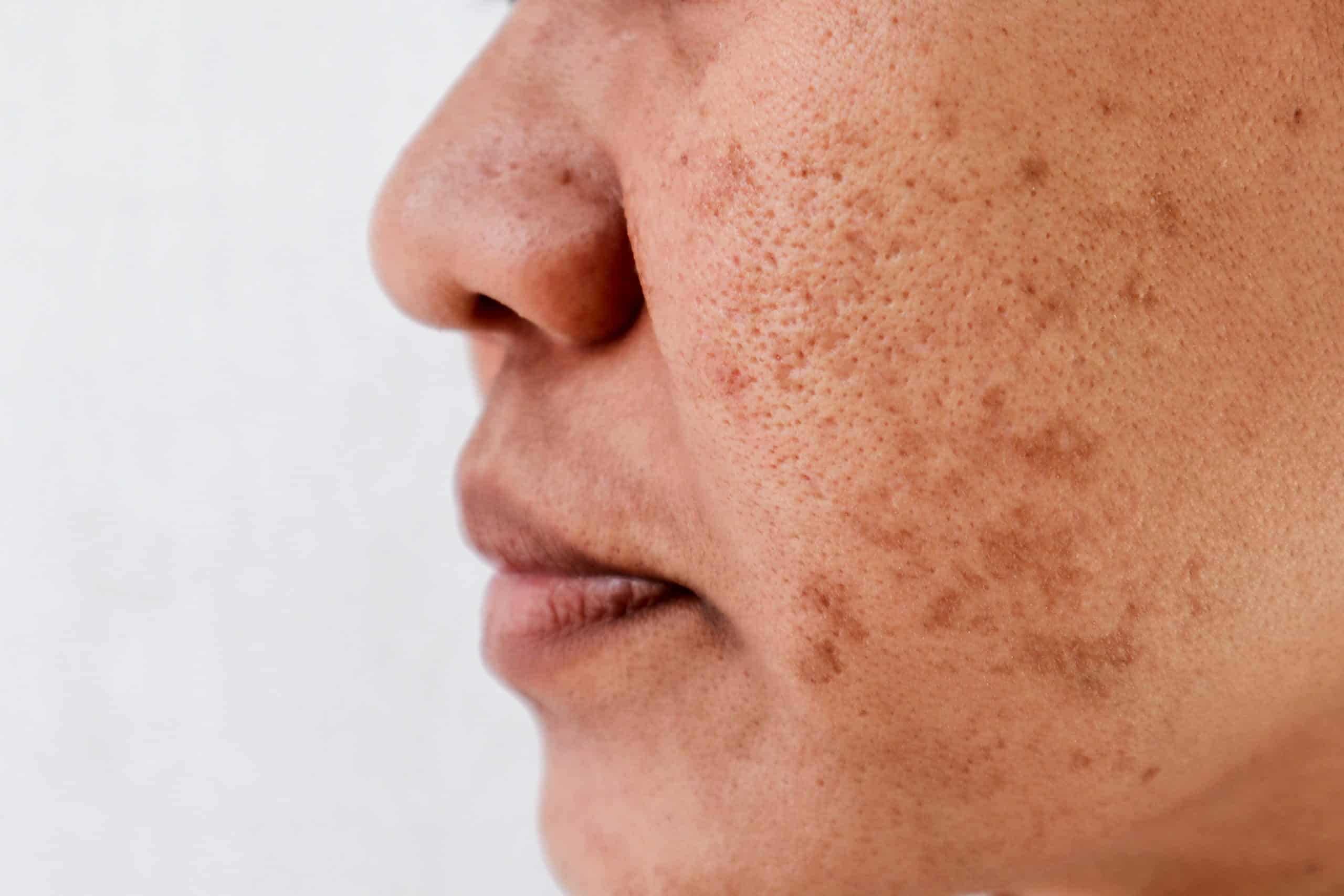
Darker spots or patches
Therapeutic options for pigmentary disorders involve a diagnosis of the underlying condition, and treatment will need to address the respective conditions.
It is important to differentiate these common benign conditions from, from more sinister causes such as skin cancers or skin manifestations of underlying systemic diseases. Therefore, a thorough evaluation is required by a dermatologist
Book an appointment with our expert dermatologists. Please select your preferred clinic below.